24/2/2023
(Partially citing Wikipedia)①
Laser cutting is a high-tech developed in recent decades. Compared with traditional mechanical cutting, it has higher cutting precision, lower roughness, higher material utilization and higher production efficiency. Especially Especially in the field of fine cutting, laser cutting has incomparable advantages over traditional cutting.
Laser cutting is a high-tech developed in recent decades. Compared with traditional mechanical cutting, it has higher cutting precision, lower roughness, higher material utilization and higher production efficiency. Especially Especially in the field of fine cutting, laser cutting has incomparable advantages over traditional cutting.
1) The principle of laser cutting(Laser Cutting Technology)
Laser cutting is to irradiate the workpiece with a focused high-power density laser beam. The temperature of the workpiece at the laser action point rises sharply. After reaching the boiling point or melting point, the material begins to vaporize or melt and form holes. With the relative movement of the laser beam and the workpiece, The final material is cut, and the slag at the cut is blown off by a certain auxiliary air flow.
Vaporization and melting are the general forms of metal material processing. When processing metal sheets, according to the laser cut section, the processing of metal materials can be divided into two parts. The first part is the vaporization of the metal, and the second part is the melting of the metal. Vaporizing metal requires high energy. Depending on the heat source, the energy for melting metal materials may come entirely from laser energy, or part of it may come from laser energy, and the other part may come from the reaction heat released by metal oxidation. Therefore, laser cutting can be roughly divided into the following three methods: laser vaporization cutting, laser melting cutting, and laser oxygen-assisted combustion cutting.

Figure 1.4 shows the schematic diagram of the laser cutting process
(1) Laser vaporization cutting (Laser Cutting Technology)
Laser vaporization cutting is to irradiate the workpiece with a focused high-power density laser beam. The temperature of the workpiece at the laser action point rises sharply. After reaching the boiling point, the material begins to vaporize: the vaporized material is cooled by the axial-assisted gas. The slag is blown off by the auxiliary gas breaker, and holes are formed on the surface of the workpiece; with the relative movement between the laser beam and the workpiece, the final material can be cut.
During laser vaporization cutting, the cut material is discharged in the form of vapor or slag, which is the basic form of cutting non-flammable materials such as wood, carbon and some plastics. When a pulsed laser is used, its peak power density is at 10° W/om? Above, all kinds of metal and non-metal materials (ceramics, quartz) are mainly removed in the form of vaporization, because at such a high laser power density, the temperature of the irradiated material will rise rapidly to the boiling point without significant melt.
(2) Laser melting cutting(Laser Cutting Technology)
Laser melting cutting is to use the focused high-energy-density laser beam to heat and melt the plate, and then blow off the molten material to form a small hole through the high-pressure non-oxidizing auxiliary gas (nitrogen, blood gas) coaxial with the beam. , with the relative movement of the laser beam and the workpiece, the final material can be cut to obtain a continuous kerf.
The high-pressure non-oxidizing auxiliary gas that does not react with the processed material is used in the laser melting cutting process, and it only undertakes the role of blowing off the molten material during the cutting process. Because the non-oxidizing gas itself is stable in nature and does not participate in the reaction of the material, the cutting section of this cutting method will not be oxidized, and even the cut workpiece can be used directly without secondary processing under certain working conditions, for example, it can be directly For welding etc.
Laser melting cutting is the basic form of sheet metal cutting, and vaporization and melting are the two basic forms of material flow during laser cutting. When the laser power density is between the melting and vaporization min values, the material will melt under the action of the laser. The vaporized material can be directly detached from the matrix material, while part of the molten material is detached from the matrix material under the action of the auxiliary gas, and part of it undergoes secondary condensation. The ratio of material vaporization mass to melting mass is called vapor-melt ratio. During laser processing, the thinner the sheet, the higher the vapor-to-melt ratio; the thicker the sheet, the lower the vapor-to-melt ratio. Studies on the cutting quality of aluminum alloys have shown that: the higher the steam-to-melt ratio, the less dross at the bottom of the cut, and the lower the frequency of dross; the lower the steam-to-melt ratio, the more dross, and the higher the frequency of dross , and relatively thick.
(3) Laser oxygen combustion cutting (Laser Cutting Technology)
Laser oxygen-assisted combustion cutting is that after the focused laser is irradiated on the plate, the material undergoes oxidation-reduction reaction under the action of laser and oxidizing auxiliary gas, and melts under the joint action of laser energy and reaction heat, and then is assisted by the coaxial beam. The gas (oxygen, air, etc.) blows off the molten material to form a through hole, and with the relative movement of the laser beam and the workpiece, the final material can be cut to obtain a continuous slit (Figure 1.5).
When oxygen-assisted cutting of steel plate, about 60% of the energy required for cutting comes from the oxidation reaction of iron. assisted by oxygen
When cutting titanium alloy plates, the exothermic reaction provides about 90% of the energy.
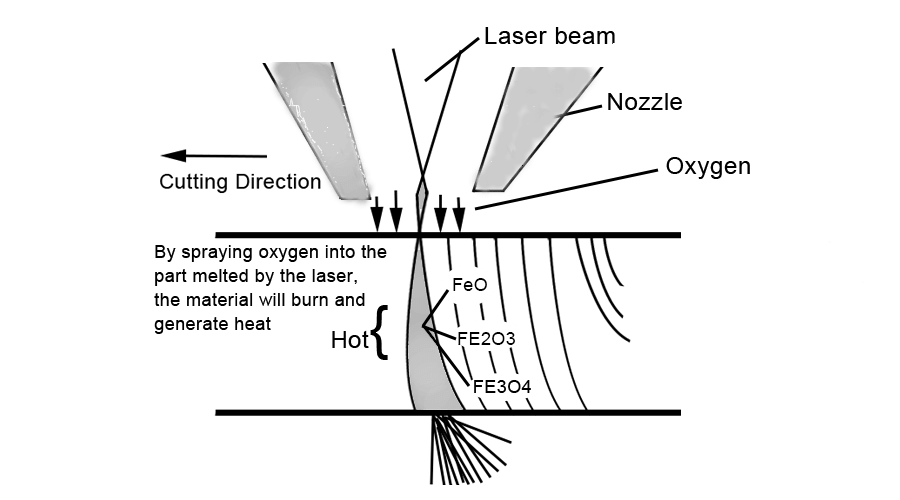
(1.5)Laser Oxygen Combustion Cutting